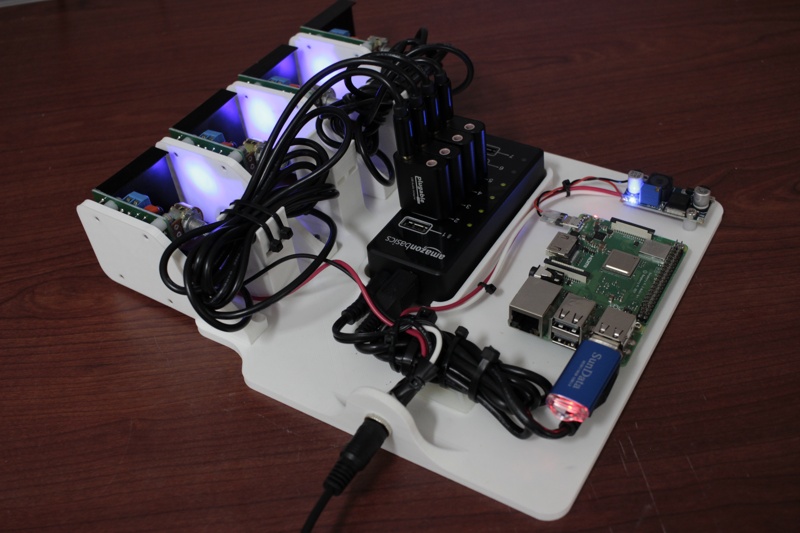

有想过用一台主机给不同的设备同时播放不同的音频文件吗?如果你正准备搭建一个DJ应用,需要实现一副耳机和一组扬声器的混音效果;又或者你需要构建一组包含许多个扬声器的音乐系统,而每个扬声器都需要播放不同的音频文件,彼此之间需要实现同步……
下面这个 DEMO 演示了用树莓派驱动8个不同的扬声器,分别播放8种不同的单声道音频文件,不仅有视频,更有必要的说明:
下面是所用的的零部件清单。
所需要的项目源代码在这里:
https://github.com/esologic/pear
参照图片连接树莓派、USB 声卡、功放、USB HUB、扬声器和电源。
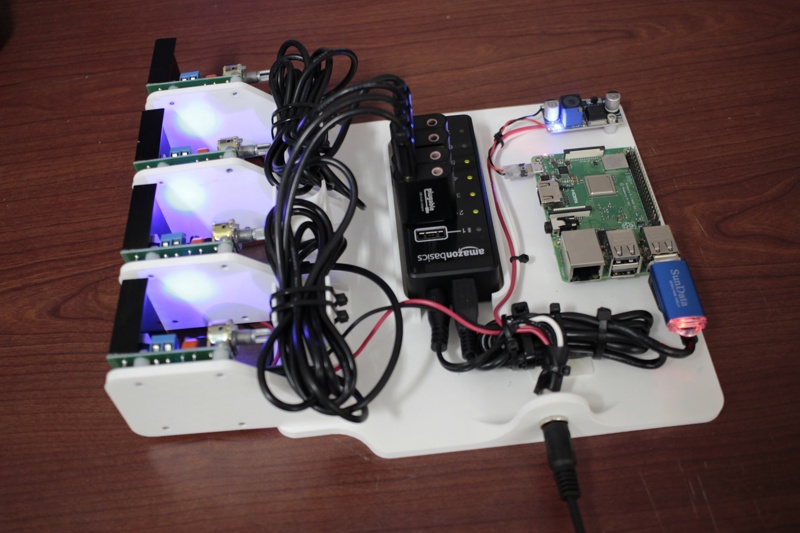


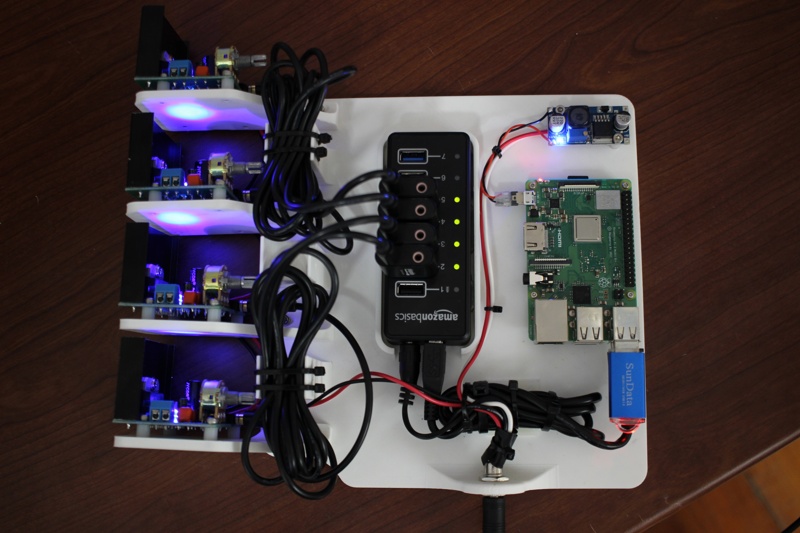

Multi-Audio 范例
首先给树莓派安装 sounddevice,用下面的命令即可。
sudo apt-get install python3-pip python3-numpy libportaudio2 libsndfile1 python3 -m pip install sounddevice soundfile
这里有4个音频文件,和 multi.py 在同一个目录下,目录结构如下。
multi_audio/ ├── 1.wav ├── 2.wav ├── 3.wav ├── 4.wav └── multi.py
这段代码基于 Python 的 sounddevice 库。
"""
multi.py, uses the sounddevice library to play multiple audio files to multiple output devices at the same time
Written by Devon Bray (dev@esologic.com)
"""
import sounddevice
import soundfile
import threading
import os
DATA_TYPE = "float32"
def load_sound_file_into_memory(path):
"""
Get the in-memory version of a given path to a wav file
:param path: wav file to be loaded
:return: audio_data, a 2D numpy array
"""
audio_data, _ = soundfile.read(path, dtype=DATA_TYPE)
return audio_data
def get_device_number_if_usb_soundcard(index_info):
"""
Given a device dict, return True if the device is one of our USB sound cards and False if otherwise
:param index_info: a device info dict from PyAudio.
:return: True if usb sound card, False if otherwise
"""
index, info = index_info
if "USB Audio Device" in info["name"]:
return index
return False
def play_wav_on_index(audio_data, stream_object):
"""
Play an audio file given as the result of `load_sound_file_into_memory`
:param audio_data: A two-dimensional NumPy array
:param stream_object: a sounddevice.OutputStream object that will immediately start playing any data written to it.
:return: None, returns when the data has all been consumed
"""
stream_object.write(audio_data)
def create_running_output_stream(index):
"""
Create an sounddevice.OutputStream that writes to the device specified by index that is ready to be written to.
You can immediately call `write` on this object with data and it will play on the device.
:param index: the device index of the audio device to write to
:return: a started sounddevice.OutputStream object ready to be written to
"""
output = sounddevice.OutputStream(
device=index,
dtype=DATA_TYPE
)
output.start()
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
def good_filepath(path):
"""
Macro for returning false if the file is not a non-hidden wav file
:param path: path to the file
:return: true if a non-hidden wav, false if not a wav or hidden
"""
return str(path).endswith(".wav") and (not str(path).startswith("."))
cwd = os.getcwd()
sound_file_paths = [
os.path.join(cwd, path) for path in sorted(filter(lambda path: good_filepath(path), os.listdir(cwd)))
]
print("Discovered the following .wav files:", sound_file_paths)
files = [load_sound_file_into_memory(path) for path in sound_file_paths]
print("Files loaded into memory, Looking for USB devices.")
usb_sound_card_indices = list(filter(lambda x: x is not False,
map(get_device_number_if_usb_soundcard,
[index_info for index_info in enumerate(sounddevice.query_devices())])))
print("Discovered the following usb sound devices", usb_sound_card_indices)
streams = [create_running_output_stream(index) for index in usb_sound_card_indices]
running = True
if not len(streams) > 0:
running = False
print("No audio devices found, stopping")
if not len(files) > 0:
running = False
print("No sound files found, stopping")
while running:
print("Playing files")
threads = [threading.Thread(target=play_wav_on_index, args=[file_path, stream])
for file_path, stream in zip(files, streams)]
try:
for thread in threads:
thread.start()
for thread, device_index in zip(threads, usb_sound_card_indices):
print("Waiting for device", device_index, "to finish")
thread.join()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
running = False
print("Stopping stream")
for stream in streams:
stream.abort(ignore_errors=True)
stream.close()
print("Streams stopped")
print("Bye.")
运行之后将分别在3个设备上播放 1.wav、2.wav 和 3.wav 音频文件。



可以看一下猿人学网站的python教程